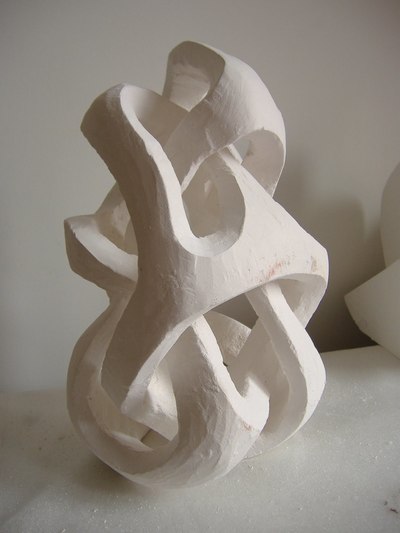
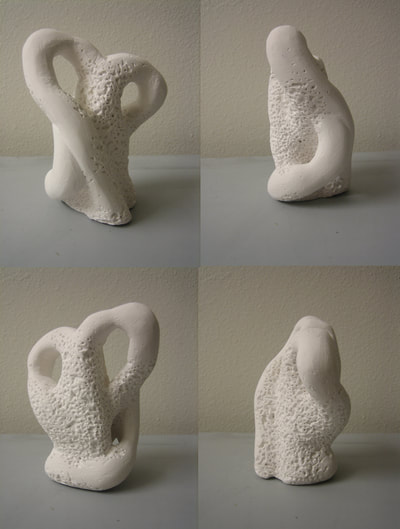
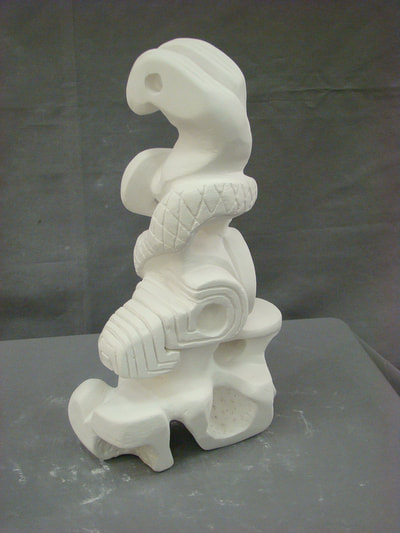
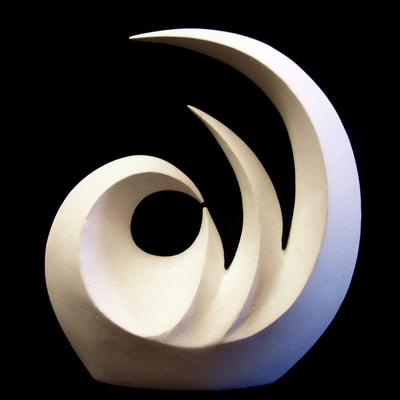
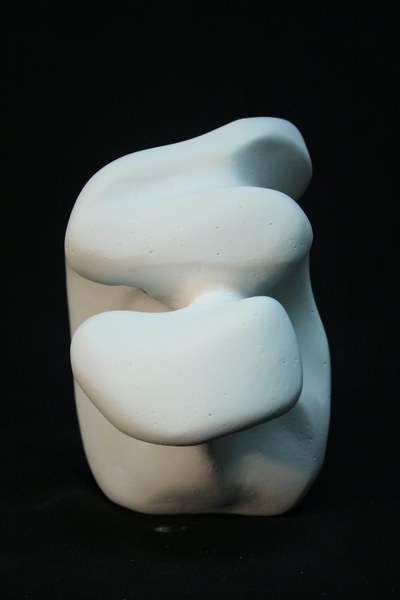
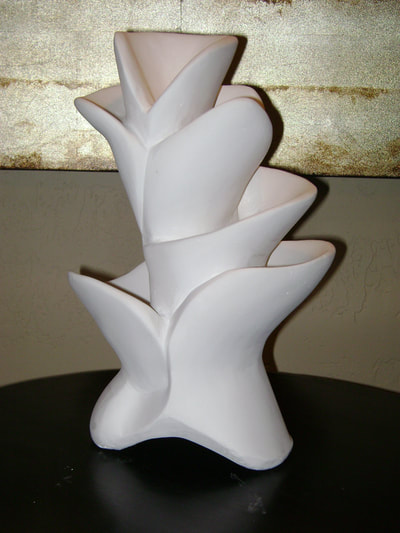
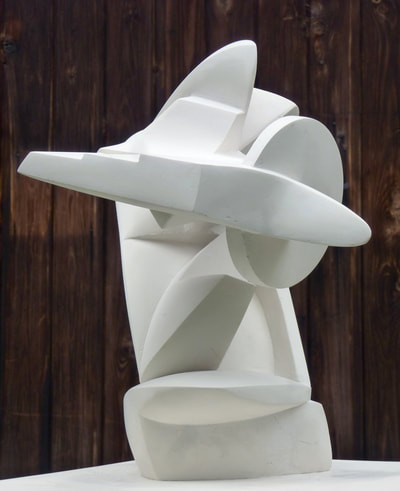
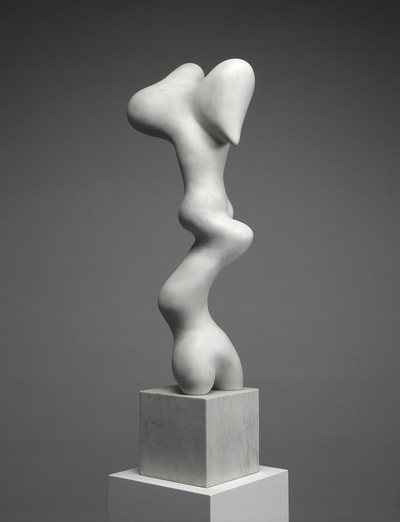
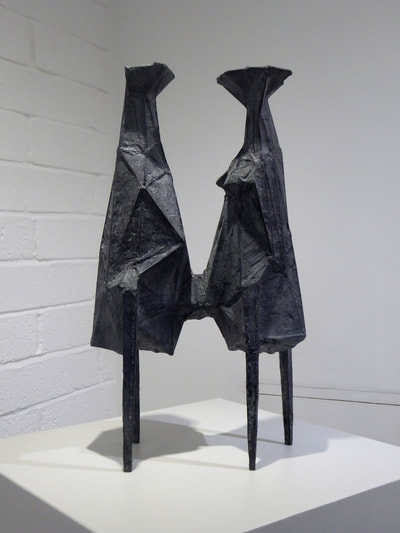
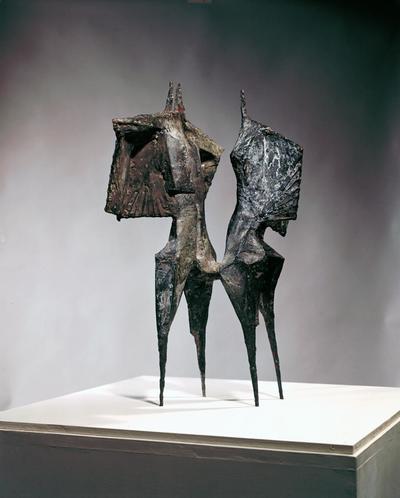
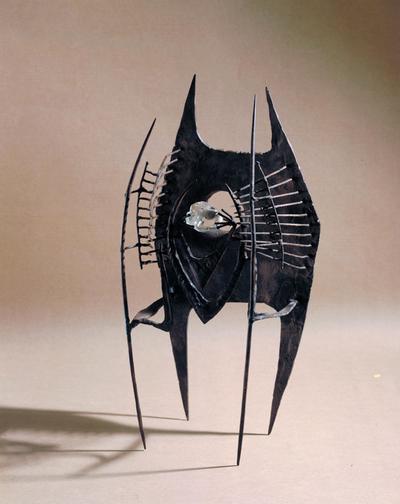
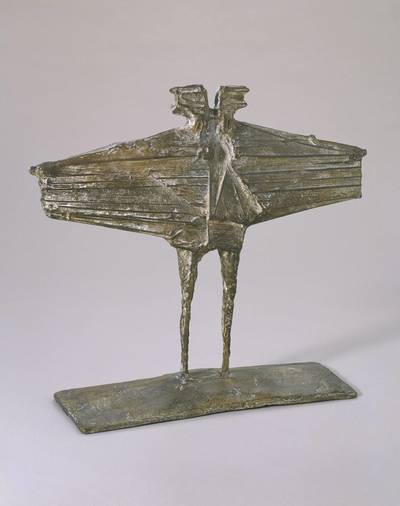
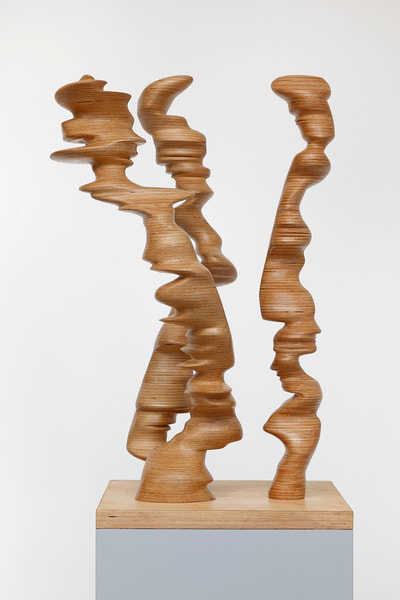
Plaster Carving: Abstraction Morphing
Your Mission:
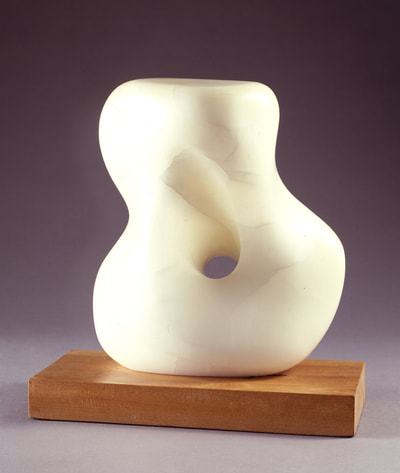
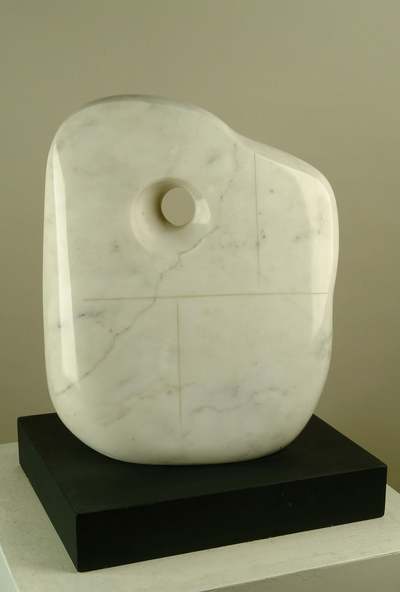
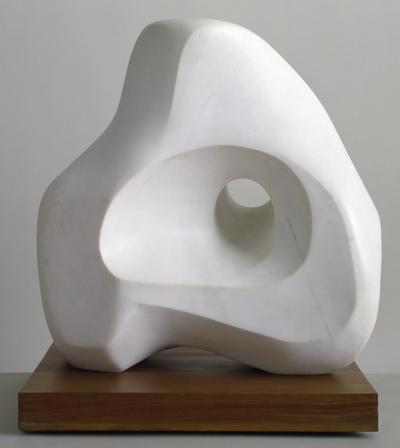
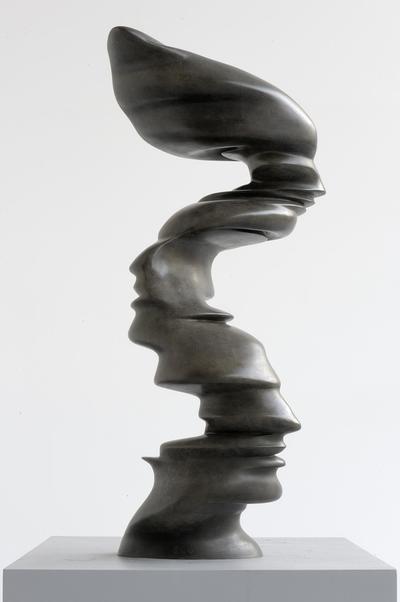
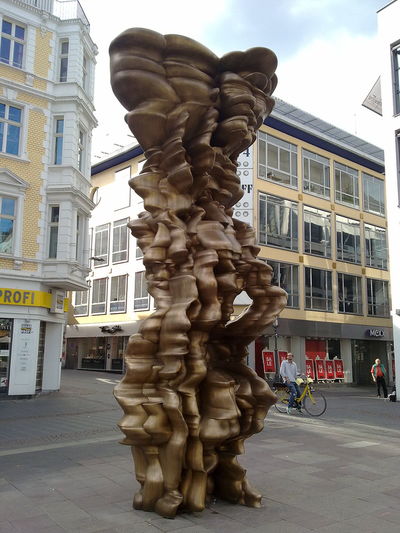
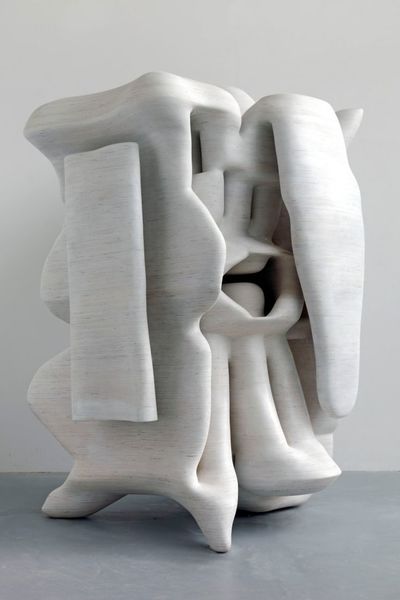
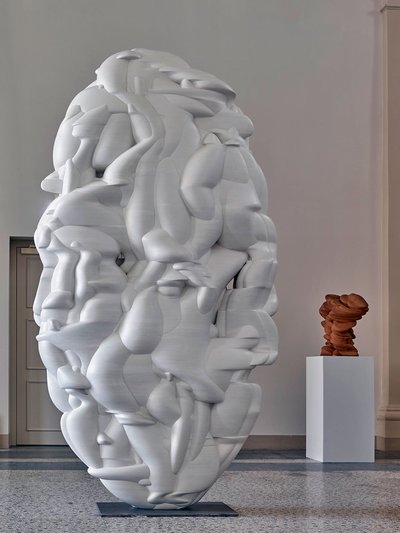
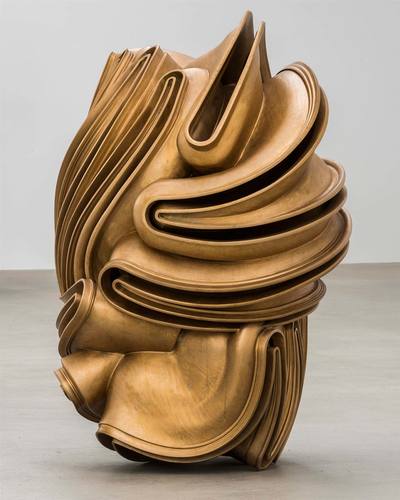
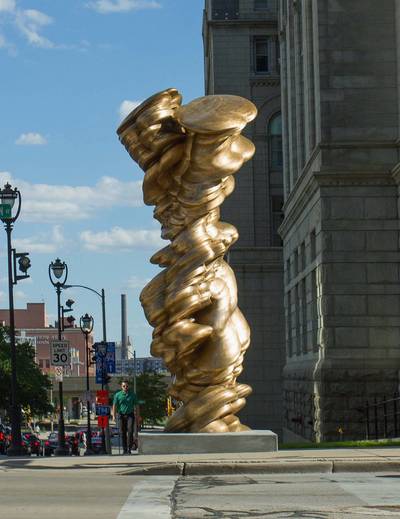
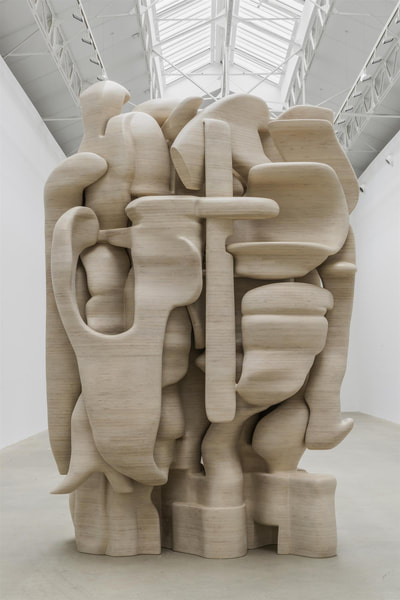
Using two forms build one, morphing the forms together to become a non-objective or abstract formal composition. The original forms are to be used as inspiration to assist in guiding the form. Use elements from each, yet develop your sculpture as a unique entity with an elegant form and a clean aesthetic. Original chosen objects may be mechanical (man-made) or natural.
Using two forms build one, morphing the forms together to become a non-objective or abstract formal composition. The original forms are to be used as inspiration to assist in guiding the form. Use elements from each, yet develop your sculpture as a unique entity with an elegant form and a clean aesthetic. Original chosen objects may be mechanical (man-made) or natural.
- Bring two interesting objects from home, which are approximately the size of your hand. Objects may be mechanical or organic.
- Create a blank from plaster.
- Brain storm and Sketch ideas.
- Plaster Carving: Create an abstract form from objects and sketches.
- Clay may be used as a modeling/sketching tool: Sketches do not always start in the sketch book. Model, in clay an abstract form, drawing characteristics from your two objects. This will assist you in developing the composition. Images of these moquettes may be placed in your sketchbook and are valid sketches.
- This project relies on the elements of light and shadow. Carve so that light and shadow create the dynamics of the form. No paint, pigments or inks should be used for this project.
- Use repetition, directional curves and form to create a since of movement.
- Develop a composition with movement that will draw the viewer around and into the form.
- Use models, sketches and your own intuitive inspirations to create. Process will play a great part in your exploration as you learn the material, developing carving techniques and sensibilities.
- Think about how these objects work together to create one form or how one may seem to dominate over the other, seeming to swallow or assimilate.
- Craftsmanship: Elegant form and a clean aesthetic should be a goal.
- Pay attention to building a form that has interior definition as well as exterior. Carving and modeling in the interior of the object will challenge your abilities, as always you are encouraged to push beyond the average.
- Do not leave any indication of the container of your original form. Work the whole form.
- Remember its okay to go back to sketches drawn or sculpted to alter and redesign your composition as you work through the project. This is a part of the process.